The term “woke” has become central in discussions about social justice, identity, and politics. While its meaning has evolved, one group stands out for embracing woke ideology more than others: young women. Understanding why young women are more woke involves exploring the origins, implications, and current usage of the term and examining the factors leading to this trend.
Definition and Origins of the term “Woke”
“Woke” originated in African American Vernacular English (AAVE), meaning to be awake or alert to social and political issues, particularly those related to race and discrimination. The phrase “stay woke” was used to encourage awareness about societal injustices. Over time, this term has broadened to include a wider range of social justice issues.
In his book, Eric Kaufmann provides a concise definition: “Woke is the making sacred of historically marginalized race, gender, and sexual identity groups.” This definition highlights that being “woke” involves recognizing and prioritizing the experiences and rights of marginalized communities.
Emergence of Single Woke Females (SWFs)
The emergence of Single Woke Females (SWFs) represents a notable demographic shift in contemporary social and political landscapes, particularly among millennials and Gen Z.
Studies indicate a growing trend where unmarried women, primarily millennials and Gen Zers, are increasingly identifying with progressive values and ideologies. This demographic cohort is characterized by its active engagement in social justice causes, advocacy for marginalized communities, and support for policies promoting equality across various social dimensions.
SWFs exhibit robust political participation, including high voter turnout in elections. They are instrumental in driving voter registration campaigns, grassroots organizing efforts, and digital activism through social media platforms. This demographic’s collective voice amplifies demands for policy reforms addressing systemic inequalities and discrimination.
The Shift in Moral Order
Kaufmann describes the rise of woke ideology as a significant change in our moral values. From this shift, a new ideology has emerged, characterized by two main pillars: emotional safety and absolute equality. This means that anything perceived as offensive to these sacred groups can result in severe social backlash or “cancelation.” SWFs are influenced by cultural shifts that prioritize inclusivity, diversity, and social equity. They are often early adopters of new social norms and are vocal proponents of challenging traditional gender roles and societal expectations. This group embraces intersectional feminism, viewing issues through a lens that acknowledges the interconnectedness of race, gender identity, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status.
For example, any comment that could be interpreted by the most sensitive member of a marginalized group as offensive can lead to accusations of blasphemy against the sacred. This is what leads to cancel culture, where individuals are ostracized for perceived transgressions against these values. Beyond individual activism, SWFs prioritize community building and creating safe spaces for marginalized groups. They engage in allyship with other social justice movements, fostering solidarity across intersecting identities and promoting collaborative efforts toward collective liberation.

Emotional Safety and Absolute Equality
Kaufmann identifies two main components of woke ideology:
- Emotional Safety: The belief that historically marginalized groups should be protected from any form of offense. This often results in calls for censorship or the silencing of dissenting voices to ensure that these groups are not subjected to emotional harm.
- Absolute Equality: The drive for complete equality in terms of representation and resources among different identity groups. This includes achieving equal representation in boardrooms, elite universities, and other positions of power, regardless of historical or contextual factors.
- Cultural Narratives: SWFs contribute to reshaping cultural narratives by challenging mainstream media representations and advocating for more inclusive and accurate portrayals of diverse identities. Their influence extends beyond politics into popular culture, influencing consumer trends, media content, and corporate social responsibility practices.
These principles reflect a deep commitment to correcting past injustices and ensuring that marginalized communities are treated with utmost respect and consideration.
Bottom-Up Emotional Drive
Kaufmann argues that woke ideology is not a top-down, systematic philosophy like classical liberalism or Marxism. Instead, it is driven from the ground up by emotional attachment to the struggles of specific groups, such as the Black civil rights movement, Indigenous rights, and LGBTQ+ rights. This emotional drive is rooted in a deep empathy and romanticization of these groups’ struggles.
This perspective emphasizes that woke ideology is more about concrete emotional attachments than abstract ideas. It is this ground-up, emotionally-driven nature that makes it resonate so deeply with many people, especially young women.
Elon Musk and the “Woke Mind Virus”
Elon Musk has become a prominent figure in the debate surrounding “wokeness,” a loosely defined term often used to criticize progressive social and political views. He said to Jordan Peterson that his estranged transgender daughter (Formerly Named Xavier) was “killed” by the “woke mind virus” after he was tricked into agreeing to gender-affirming care procedures. Musk has employed the term “woke mind virus” to describe what he perceives as an excessive focus on social justice issues to the detriment of other concerns.
The term gained significant attention following a public dispute with his daughter, Vivian Jenna Wilson, who transitioned from male to female. Musk attributed his daughter’s transition to the influence of what he termed the “woke mind virus.” This claim sparked widespread debate and criticism, with many accusing Musk of transphobia and misrepresenting the complexities of gender identity.
Musk’s use of the term “woke mind virus” has become a rallying cry for some who share his views, while others see it as a divisive and harmful attack on progressive values. The phrase has entered the broader cultural lexicon, often used as a shorthand for criticizing social justice activism and identity politics. He ended the talk with saying “I was tricked into doing this,” Musk said. “I lost my son, essentially. They call it ‘deadnaming’ for a reason. The reason they call it ‘deadnaming’ is because your son is dead.”
Liberal Progressivism and Emotional Influence
In discussions about the origins and spread of woke ideology, several causal elements are often highlighted:
- Liberal Progressivism: This historical movement, beginning in the early 20th century, emphasized social justice and equality. Over time, its principles have influenced contemporary woke ideology, which seeks to expand and enforce these values more rigorously.
- Compassion and Emotion: Woke ideology is heavily driven by compassion and emotional responses to perceived injustices. This is why it resonates so strongly with younger generations and why it often leads to passionate advocacy for change.
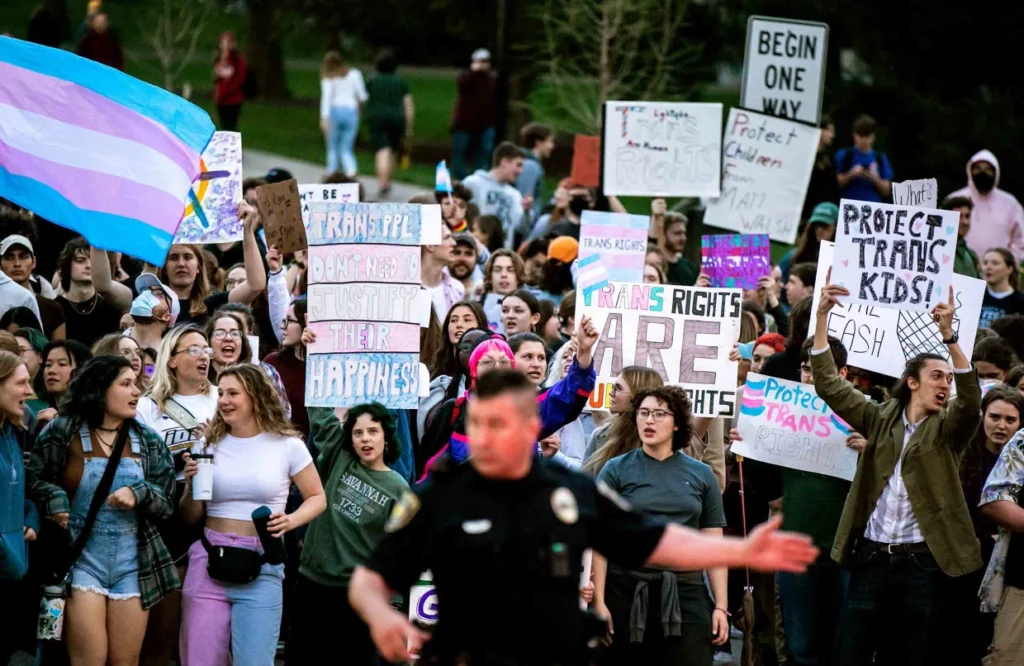
Marxism and Victim-Victimizer Narratives
Another significant influence on woke ideology is Marxist thought, which traditionally divides society into oppressors and oppressed based on economic class. In contemporary woke ideology, this framework has been expanded to include other dimensions of identity, such as race, gender, and sexuality. This means that society is now seen as divided into victims and victimizers across multiple axes of inequality.
This framework is used to justify the need for absolute equality and the protection of marginalized groups from any form of offense or harm.
The Role of Higher Education in adopting Woke Belief.
The role of higher education in shaping “woke” beliefs among women is a topic of ongoing discussion, highlighting various influences and complexities. Research has shown that certain predictors increase the likelihood of adopting woke beliefs, including low verbal intelligence, being female, having a female temperament, and exposure to politically correct courses. The increasing dominance of women in higher education, especially in the humanities and social sciences, has also been linked to the spread of woke ideology. This environment supports discussions on social justice and identity politics, empowering women to develop informed perspectives and advocate for change.
While there is a perception that some university faculty lean towards progressive viewpoints, higher education emphasizes the development of critical thinking skills. This emphasis enables women to independently evaluate arguments, form their own opinions, and engage in respectful debate, even when perspectives differ from those of their instructors.
This trend reflects a broader cultural shift, as universities and other institutions become more influenced by these values. For example, political donations from highly educated individuals have increasingly shifted towards progressive causes since the early 2000s.
It is essential to prioritize the free exchange of ideas within universities. This approach fosters environments where respectful debate can flourish, crucial for nurturing academic excellence and preparing women to contribute thoughtfully to an inclusive society. Ultimately, higher education aims to equip women with the skills and knowledge necessary to engage with complex societal issues in a nuanced and informed manner, fostering empowerment and societal progress.
Gender Dynamics and Ideological Support
Women, particularly young women, have been found to support woke ideology more than other demographic groups. However, this support is nuanced. For instance, while women are less likely than men to support violent measures to silence dissent, they are more likely to advocate for emotional safety and the protection of marginalized groups from offensive speech.
Kaufmann argues that women’s support for woke ideology is influenced by societal norms and the dominant moral order. Historically, women have tended to reinforce the prevailing values of their society, whether those are religious, patriotic, or progressive.
The Role of Social Media

Raised in the era of digital communication, SWFs harness social media to mobilize support, raise awareness, and organize protests or demonstrations. Platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok serve as powerful tools for amplifying their voices and connecting with like-minded individuals globally.
Social media platforms played a significant role in spreading woke ideology, particularly among younger generations. The rapid dissemination of short, emotionally charged videos can amplify messages of compassion and social justice, further entrenching these values in the minds of young people.
Conclusion
The term “woke” encapsulates a complex and evolving set of beliefs centered on social justice and the protection of marginalized groups. Young women are more woke due to a combination of educational influences, emotional drives, societal norms, and the pervasive impact of social media. Understanding the full context and implications of woke ideology is essential for navigating the ongoing debates about its role in society and the reasons behind its particular resonance with young women.
References:
- Kaufmann, E. (n.d.). Definition and Discussion of “Woke”. Retrieved from Eric Kaufmann’s Book
- Historical Origins of “Woke”. (n.d.). Retrieved from Etymology Online
- Political Donations and Ideological Shifts. (n.d.). Retrieved from Pew Research Center
- Influence of Social Media on Woke Ideology. (n.d.). Retrieved from Manhattan Institute Studies
- Gender Dynamics in Support for Woke Ideology. (n.d.). Retrieved from Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression


